Al-Fārābī’s (872-950 AD) views on the different phases of the intellect are to be found in The Treatise on the Intellect (Risālah fi’l-‘aql). He borrows the idea from Alexander (however, he wrongly attributes it to Aristotle) that the human intellect’s evolution progresses in three phases: material, actual, and acquired. For the realization of the last – acquired – phase, the help of higher, non-human intellect – the active intellect is needed (see also [3.2.2]).
These phases are presented in the following OntoUML diagram:
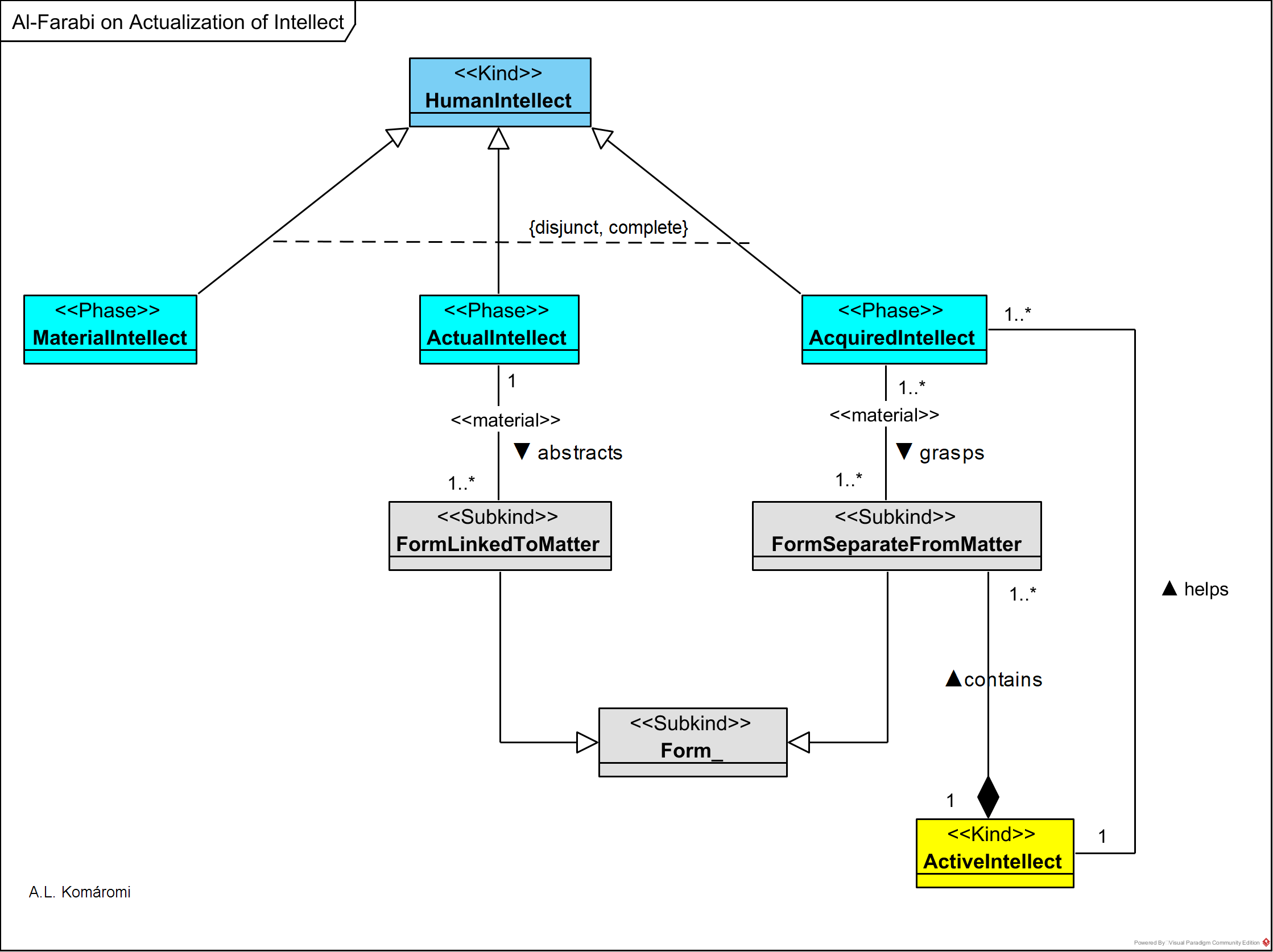
| Class | Description | Relations |
| HumanIntellect | Human intellect (arabic: aql, greek: νοῦς) “is understood as a faculty of the soul by means of which certainty about necessary, true, and universal premises is attained. Premises of this kind are not arrived at by means of syllogisms, but are present in the subject in a prior way, either by nature or without one being aware of how these premises were acquired. Hence, this faculty is some part of the soul by which humans have access to the first principles of the theoretical sciences.” | |
| MaterialIntellect | Material intellect (arabic:‘”aql bi-l-quwah“): “Following Aristotle and the Aristotelian tradition, al-Fārābī describes the intellect as being itself potential or, using Alexander’s terminology, an innate ‘natural disposition’ […]. This kind of intellect is frequently called “potential”, “material”, or “passive”, and is simply the rational faculty with which all human beings are endowed. In The Treatise on the Intellect al-Fārābī refers to the material intellect (νοῦς ὑλικὸς, a Greek term coined by Alexander) as a soul or part of the soul, or one of the faculties of the soul, or something that is in potency to abstract the forms from their matter and turning these into forms for itself” | is phase of HumanIntellect |
| ActualIntellect | Actual intellect (arabic: ‘aql bi’l-fi‘l): “When these forms are abstracted, they become intelligibles or forms for the material intellect. It can be rightly said that for al-Fārābī the material intellect is like the matter where the abstracted forms come to be, where the material intellect itself becomes the abstracted forms, just as the imprinted object leaves its mark on a piece of wax. Before a form of the objects outside the soul has been abstracted, the material intellect is just in potency to receive those forms or potential intelligibles; but when these latter come to be in the material intellect, the material intellect becomes an actual intellect, and the potential intelligibles are actualized. Now, the existence of actual intelligibles is different from their existence as potential intelligibles or forms in matter. When external to the soul and linked to matter, forms are affected by place, time, position, quantity, and the like. But when forms are actualized in the soul, many of these qualities are removed and their existence thus becomes different from their former existence as forms of bodies outside the soul.” | is phase of HumanIntellect; abstracts FormLinkedToMatter |
| AcquiredIntellect | Acquired intellect (arabic: ‘aql al-mustafāḍ): “the process of abstraction is not required in the case of forms separate from matter, that is, the separate entities that belong to the supralunar realm. These separate forms are grasped by the intellect not as actual intellect but as the acquired intellect, and thus become forms for it. Moreover, the acquired intellect is a perfection of the human intellect because it has no need to perform the activity of abstraction in order to grasp forms existing separately from matter. In other words, it is the acquired intellect that enables the grasping of separate forms through the assistance of the active intellect.” | is phase of HumanIntellect; grasps FormSeparate FromMatter |
| Form | Form (arabic: ‘aql al-fa ‘‘āl): “In The Political Regime al-Fārābī deals with the relation between matter and form, and explains that form is the actualization of matter in the sense that form is more excellent than matter; however, matter is the substratum of form and without matter there is no form […]. As can be seen, al-Fārābī is a partisan of Aristotelian hylomorphism” (see also [1.3.5]) | |
| FormLinkedToMatter | Forms linked to matter are external to the soul, and “are affected by place, time, position, quantity, and the like. […] forms linked to matter have to be abstracted in order to become actual intelligibles in the actual intellect.” | is subkind of Form |
| FormSeparate FromMatter | Forms separate from matter can be e.g. the forms of celestial bodies (see [3.2.1]): “the process of abstraction is not required in the case of forms separate from matter, that is, the separate entities that belong to the supralunar realm.” | is subkind of Form |
| ActiveIntellect | Active intellect is emanated by the second intellect (see [3.2.1]), and helps the grasping of forms separated from matter by the acquired intellect. | contains FormSeparate FromMatter; helps AcquiredIntellect |
Sources
- All citations from: López-Farjeat, Luis Xavier, “Al-Farabi’s Psychology and Epistemology”, The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy (Summer 2018 Edition), Edward N. Zalta (ed.)
First published: 6/2/2020

